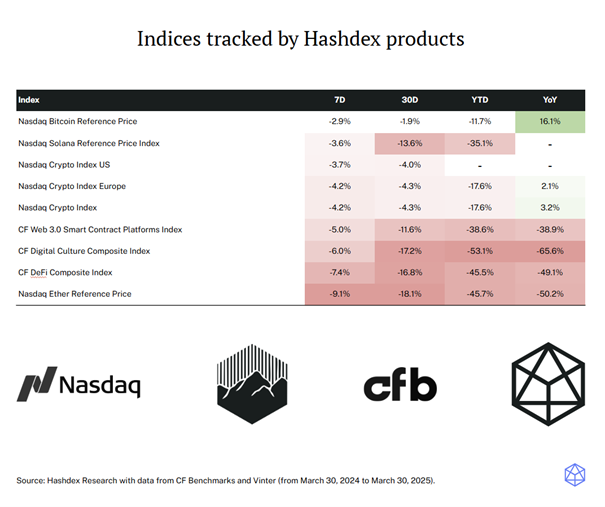
A question that is frequently asked is whether Ethereum will ever be replaced by another network. This question often comes alongside inquiries about the key differences between Layer-1 networks and their approaches to addressing the challenges Ethereum has introduced to the world of crypto.
To recap, a Layer-1 blockchain is the foundational layer responsible for handling consensus and the execution of transactions and smart contracts. To make it easier to understand, let’s categorize these type of networks into two main groups (excluding Layer-2 solutions):
- Similar networks (networks based largely on the same set of technologies or even compatible with Ethereum) with additional features. We will refer to these as EVM-compatible networks, for example: Solana, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, Tron, Toncoin, Cardano, Avalanche, NEAR.
Note: sometimes these networks are natively incompatible without additional efforts to make them compatible (such as a sidechain or a form of virtualization) but to keep complexity they are included as well.
- Novel networks (networks based largely on a new set of technologies and therefore being largely incompatible with Ethereum) with equivalent features. We can refer to them as EVM-Equivalent networks, for example: Sui, Aptos, Sei, Kaspa, Stellar, Filecoin, Hedera.
The blockchain landscape has been dominated by Ethereum for years, with its robust smart contract capabilities and widespread adoption. However, as the network continues to face scalability and congestion issues amongst other issues like security, cost and user-experience, various Layer-1 blockchains have emerged, each vying for the title of “Ethereum Killer.” Networks like Solana, Avalanche, and Cardano have all taken different approaches to outpace Ethereum, yet none have fully succeeded in dethroning the giant. When it comes to EVM-equivalent networks, Sui Network—is a new contender with rapid growth with origins from Meta’s Diem project that could be the true game-changer in the race to overcome Ethereum’s limitations.
The Rise of Layer-1 Competitors
How have other EVM-compatible networks tried to surpass Ethereum?
- Solana: Known for its high throughput, Solana uses a unique consensus mechanism called Proof of History (PoH) combined with Proof of Stake (PoS). This allows Solana to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), far surpassing Ethereum’s current capabilities. However, Solana has faced issues with network stability and centralization concerns, leading some to question its long-term viability.
- Avalanche: Avalanche offers a highly flexible platform with its Avalanche consensus protocol, which allows for sub-second transaction finality and the ability to create custom blockchains. Avalanche’s unique architecture supports interoperability between multiple chains, making it a strong contender. Yet, like Solana, it has struggled with decentralization and network congestion at scale.
- Cardano: Cardano takes a more methodical, research-driven approach, emphasizing security and scalability through its Ouroboros PoS consensus protocol. Cardano’s development has been slower, with some critics pointing to its lack of decentralized applications (dApps) and real-world usage as significant drawbacks.
EVM-Equivalent networks are taking a different approach; they are not just facing the challenge of getting users to switch for enhanced functionality, but also developers to switch to a different, potentially better, way of building decentralized applications. For example:
- Sui Network: aims to offer developers and users alike a safer, faster and more user-friendly environment for using, connecting and developing applications. It does this with a full redesign on the consensus and execution of transactions and smart contracts as well as a completely new smart contract language called Move.
The Layer-2 Conundrum: Scaling Ethereum
Ethereum has been working to address its scalability issues through the development of Layer-2 (L2) solutions like Optimism, Arbitrum, and zk-Rollups. These L2 solutions aim to offload transactions from the Ethereum mainnet, thereby increasing throughput and reducing fees. While L2 solutions offer a promising path forward, they come with trade-offs:
- Complexity: Users must interact with multiple layers, which can complicate the user experience and lead to fragmentation within the ecosystem.
- Security Concerns: Since L2 solutions rely on Ethereum’s base layer for security, they may inherit vulnerabilities and create new attack vectors.
- Limited Interoperability: L2 solutions often face challenges in maintaining seamless interoperability with other blockchains and L1 solutions.
While L2s provide a temporary solution, they may not fully resolve Ethereum’s fundamental issues. This is where a new EVM- Equivalent network such Sui Network could step in as a more comprehensive alternative. At the same time, Ethereum as a protocol is far from finished and developers may be able to tackle these obstacles towards mass adoption over time while other networks are trying to reinvent the wheel and struggle to get a critical mass.
This is not financial research but the opinion of the author of the article. We publish this information to inform and educate about recent market developments and technological updates, not to give any recommendation for certain products or projects. The selection of articles should therefore not be understood as financial advice or recommendation for any specific product and/or digital asset. We may occasionally include analysis of past market, network performance expectations and/or on-chain performance. Historical performance is not indicative for future returns.
Important information
For informational and advertising purposes only.
This information is intended only to provide general and preliminary information to investors and shall not be construed as investment, legal or tax advice. VanEck assumes no liability with regards to any investment, divestment or retention decision taken by the investor on the basis of this information. Views and opinions expressed are current as of the date of this information and are subject to change with market conditions. Certain statements contained herein may constitute projections, forecasts and other forward looking statements, which do not reflect actual results. VanEck makes no representation or warranty, express or implied regarding the advisability of investing in securities or digital assets generally.
Performance quoted represents past performance, which is no guarantee of future results and which may be lower or higher than current performance.

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedan
 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedan
 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedan
 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedan
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedan
 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedan
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedan
 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedan